Abstract
Introduction
Four cycles of bortezomib/thalidomide/dexamethasone (VTD) induction therapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is one of the standard therapy for patients aged less than 65 years with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). Complete remission (CR) status before ASCT is an important prognostic factor for progression-free survival (PFS). We analyzed whether two additional cycles of VTD improved the pre- and post-transplant responses as well as PFS compared to the four cycles of VTD induction therapy.
Methods
A total of 222 patients with NDMM between September 2014 and August 2016 from eleven hospitals in South Korea were included in the current study. The patients received at least four or more cycles of VTD induction therapy before administration of high-dose therapy (HDT, melphalan 200mg/m2) followed by ASCT. VTD regimen was consisted of bortezomib subcutaneous infusion (1.3 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, and 11), thalidomide (100 mg daily), and dexamethasone (40 mg on days 1-4, 8-11), which was administered every 4 weeks.
Results
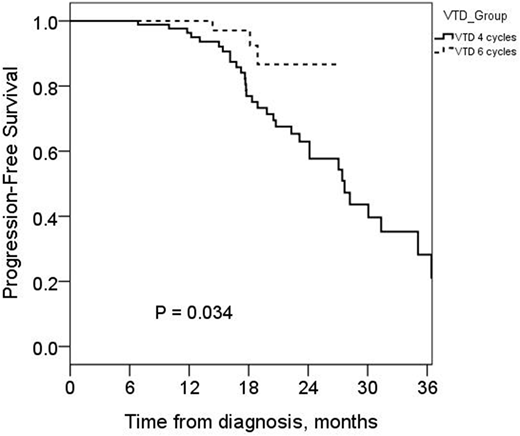
The median age was 57 years (range 30−64 years), and 120 patients (61.9%) were male. Revised international scoring system (R-ISS) classified 59 (30.4%), 86 (44.3%), and 49 patients (25.3%) as stage I, II, and III, respectively. VTD induction was administered 4 cycles in 194 patients (VTD4, 67.5%) and more than 4 cycles in 63 (VTD6, 32.5%) before HDT. Patient characteristics at diagnosis did not differ between VTD4 and VTD6. CR rate before HDT was significantly higher in VTD6 than VTD4 (31.7% vs 13.0%, P = 0.003). However, CR rate after HDT/ASCT was similar between VTD4 and VTD6 (69.0% vs 65.5%, P = 0.726). There was no difference in the incidence of peripheral neuropathy (PN) (≥ grade 2 or that required dose reduction) between two groups. The median follow-up duration was 18.0 months (range 7.0-43.8 months). The 2-year PFS did not differ between the two groups (51.7 ±5.7% in VTD4 and 62.1±8.6% in VTD6, P = 0.240). Multivariate analysis revealed that the achievement of CR was a favorable prognostic factor for PFS (HR 0.27 [0.08−0.90], P = 0.034). Deletion 17p (HR 2.87 [1.01−7.92], P = 0.048) and t(4;14) (HR 3.38 [1.76−6.48], P < 0.001) in FISH were adverse prognostic factors for PFS. Patients with stage I/II by R-ISS receiving additional two cycles of VTD showed prolonged PFS (median PFS not reached vs. 27.6 months, P = 0.034). In the multivariate analysis, VTD6 was a favorable prognostic factor for PFS for patients with stage I/II by R-ISS, (HR 0.11 [0.02−0.52], P = 0.005).
Conclusion
CR rates increased with additional cycles of VTD induction therapy for NDMM. However, the PFS benefit was observed only in patients with R-ISS stage I/II. For patients with high-risk MM, intensive induction therapy that overcome poor prognostic factors should be administered to improve long-term outcomes.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal